Human necks, like other animals, are wonderful body parts, quite fragile but strong.
The cervical spine, along with all the muscles and ligaments, supports and mobilizes the skull, absorbs shocks while walking, protects the brain from concussions, protects mice that feed, and also protects the spinal cord.
It is arguable that almost everyone has experienced neck pain in their lifetime. Neck pain can affect men and women of any age.
When the neck hurts, the causes can be quite varied. Some resolve on their own within a few days, while others can cause chronic illness and pain.
Why does the pain occur?
The most common cause of neck pain is poor posture. With its back bent, the head ceases to be positioned just above the body and moves forward. In this situation, the muscles and ligaments of the neck experience increased tension. Prolonged absence from work, sleeping on a soft bed or high pillow, and prolonged static load promote the development of hunching and neck pain.
Other causes of neck pain include a head fall, a traffic accident, or an injury from sports. With sharp acceleration and then braking, the cervical spine performs a whiplash. As a result, the ligaments and muscles may protrude, dislocation or compression fractures occur in the cervical vertebrae, and an intervertebral hernia develops.
Neck pain can occur as a secondary manifestation of other diseases. For example, in the case of a heart attack, when the heart attack causes severe pain, it radiates along the nerve braids to the upper limbs, chest, neck. Neck pain with heart pain is only part of a large complex of symptoms - shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, vomiting. If you have a sore neck or jaw and other signs of a heart attack, call an ambulance immediately.
Cervical pain is also used as a diagnostic sign of meningitis. With this disease, the neck muscles become hypertensive, i. e. , become stiff. When you try to tilt your head to your chest, your back neck hurts badly.
The spine in the neck area is painful with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, fibromyalgia, spondylosis and osteoarthritis, hernia or protrusion, with edema, abscesses, tumors or benign tumors with compression of the nerve roots or spinal cord.
Special cases
Degenerative diseases
Osteochondrosis, or in other words, dystrophic disorders of the intervertebral discs, lead to a person’s neck constantly sore. This is usually mild aching pain, often accompanied by numbness and pain in the shoulder girdle and head.
The collar zone affected by osteochondrosis can cause the development of cerebral artery syndrome. As the intervertebral distances decrease in this area, pressure damage to the vertebral arteries occurs in the openings of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. The pressure on the vessel causes a decrease in blood flow to the brain, with dizziness, loss of vision and hearing loss. On the other hand, mechanical stimulation of the artery with pressure from the vertebrae causes reflex cramps, manifested as burning throbbing pain.
Treatment
If the neck continues to ache in the background of osteochondrosis, therapy begins with the elimination of the pain syndrome. The second mandatory direction of treatment is to stop the degenerative processes of the cervical vertebrae.
Pain relief can be achieved using the following groups of drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs — directly block the cascade of pain signaling mediators;
- muscle relaxants - eliminates muscle cramps, reflexively, resulting from severe pain;
- sedatives - soothe and inhibit the nervous system and the transmission of pain impulses, including (valerian, antidepressants, hypnotics);
- vasodilators - help eliminate vertebral artery syndrome and the pain that comes with it.
To eliminate the cause of neck pain in osteochondrosis, chondroprotective drugs are prescribed that prevent the destruction of cartilage and vertebrae, as well as multivitamin mineral complexes.
Pain management also consists of physiotherapy, physiotherapy, massage, traction, reflexology and adhesive therapy. To relieve pain during exacerbation, it is recommended that the patient wear a special collar that protects the neck from excessive mobility.
Muscle pain
Neck pain can occur when the neck muscles become inflamed, which is called myositis.
Such pain must be distinguished from neuritis (inflammation of the nerve trunk with a sensory disorder) and pain caused by osteochondrosis.
Myositis occurs as a result of sudden, predisposing factors - hypothermia, vibration, prolonged overload - especially with the same type of prolonged repetitive movements.
Cervical myositis is characterized by acute pain that occurs when the inflamed muscle contracts. The sharp severity of the pain leads to certain types of movements.
Usually, the long muscles of the neck on the anterolateral surface or the sternocleidomastoid muscles hurt, which pull the head back with bilateral contraction and reverse it with unilateral contraction.
The deep muscles surrounding the spine also often become inflamed and mobilize the entire neck and back.
Increased voice and dense nodular areas are observed when the muscle is probed. Violation of microcirculation and local trophism leads to a gradual connective tissue exchange of myocytes. As a result, the neck muscles weaken, their symmetry is broken on the side of the spine, torticollis may appear, and the patient has difficulty holding his head.
Treatment
Treatment begins by reducing the load on the neck. This is followed by physiotherapy procedures - UHF -heating, electrophoresis with drugs, heating with paraffin, ozokerite wrap, diathermy, massage, acupuncture. Such procedures restore blood circulation to the neck muscles. Among the drugs, vitamin B injections, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, ointments and rubs are prescribed.
Alternative treatment suggests using cabbage or burdock leaves as an analgesic compress, making an ointment from willow buds mixed in butter, and rubbing a mixture of turpentine, apple cider vinegar, and egg yolk. In addition, the neck is rubbed with lava oil and then wrapped. The main guarantee of success for any treatment is to keep the sore neck calm until your muscles are fully recovered. Then start them back "on duty" with special gymnastics and massage.
Radicular syndrome
Severe neck pain, which extends to the muscles of the head, shoulder girdle, upper limbs, can occur when the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched during prolapse, protrusion, or disc herniation.
With this disease, the inner core of the disc extends toward the spinal cord or its lateral horns. The hernia and its symptoms usually appear on one side. When pressure is applied to the roots of the spinal nerves, burning, sharp pain appears in the innervated muscles (cervical lumbago). The patient feels numbness in the lower jaw, the area around the ear, the back of the head, the shoulder blades, the arms. Dizziness appears, a sharp pain in the neck as it changes from a horizontal position to a vertical one. Gradual protrusion of the disc leads to damage, inflammation, and edema of the surrounding tissues. This creates the preconditions for inflammation of nerve endings with the development of radiculitis, the mobility of the neck and upper limbs is gradually limited. Prolonged damage to the spinal nerves leads to paresis or paralysis of the limbs.
Therapy
What to do if your neck hurts with a hernia? At home, with pain syndrome, they take painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal medications, muscle relaxants to relieve cramps.
In the hospital, severe pain in the neck is eliminated with the help of "blockades" - the introduction of anesthetics on the side of the spine.
Swelling and inflammation are treated with steroids that can be injected directly into the hernia. Muscle pain is eliminated by taking muscle relaxants.
Also, to prevent the hernia from developing further, I use drugs that strengthen cartilage tissue - chondroprotectors.
In many cases, therapeutic exercises for the cervical spine and pulling traction with a protrusion or a slight protrusion will help. The increase in intervertebral space helps the intervertebral disc to "retract" and relieve pressure on the nerves.
In the case of a real hernia, with rupture of the anulus fibrosus and the fall of the nucleus into the spinal cord, surgery is required. There are several ways to eliminate neck pain through surgery:
- anterior cervical discectomy - removal of an extra disc that presses on the spinal nerves;
- replacement of the damaged disc with an artificial joint that protects the cervical spine from further destruction;
- microendoscopic dissectomy with retrospective approach and removal of small areas of the hernia with an endoscope;
- posterior cervical dissectomy with incision in the back of the nape of the neck. The treatment channel has been specifically widened to prevent twists in the future.
Neoplasms
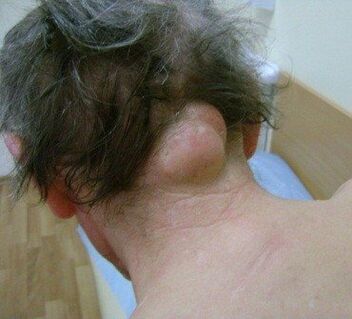
If there is constant squeezing pain in the neck, the appearance of foreign education in this department may be suspected.
Benign or malignant tumors of the neck can develop in the vertebral body, blood vessels, epithelium, connective, nerve, adipose, or glandular tissues.
Benign tumors (lipoma, fibroids, neuroma, osteoma, hemangioma) are most often properly shaped and clearly limited, rarely causing pain. The discomfort is primarily due to the compression of the surrounding tissues by the tumor. Malignant tumors (osteosarcoma, myeloma, lymph node or thyroid cancer) have no boundaries, giving many metastases to adjacent tissues. Their destructive effect on the organs causes a painful feeling and general deterioration. The front of the neck can get cancer of the larynx, throat, oral organs, thyroid. The patient has difficulty swallowing, swelling of the neck and face, changes in tone. If the cervical canal hurts with a bone tumor, this condition is often accompanied by damage to the spinal cord and nerve roots on the side of the spine with the development of paralysis.
Treatment
In neoplasms, the treatment of pain is primarily aimed at eliminating the cause - reducing or eliminating the swelling. For this purpose, chemotherapy and radiation therapy, hardening of the blood vessels supplying the tumor and surgical removal of the abnormal formation are used.
Pain relief depends on the severity of the pain:
- weak analgesics;
- moderate analgesics;
- they switch to weak opiates as the pain increases;
- in severe pain, pain relief is only possible with opiate medications. To increase the pain relief of neck pain using tumors, antipsychotics, antispasmodics and corticosteroids.
Note! Neck pain can occur for a variety of reasons. In order not to miss serious illnesses, you should first consult a doctor to consult about the occurrence of pain and the exact identification of the source.























